1. Network sniffing tools
- Cain and Abel is a collection of tools that includes ARP poisoning. Cain and Abel redirects packets from a target by forging ARP replies.
- Ettercap is a sniffing tool with multiple functions that can be used for ARP poisoning, passive sniffing, packet grabbing, and protocol decoding.
- TCPDump is a command line sniffer designed for the Linux environment.
- Ufasoft snif is a sniffing tool that has capturing, analyzing, and decryption features.
- WinDump is the windows version of TCPdump.
- Wireshark is a network packet analyzer that tries to capture network packets and display the data they carry in as much detail as possible.
- Shark is a tool that is used to create botnets.
- KFSensor is a Windows host-based intrusion detection system. It acts as a vulnerable server to attract hackers and record their activities.
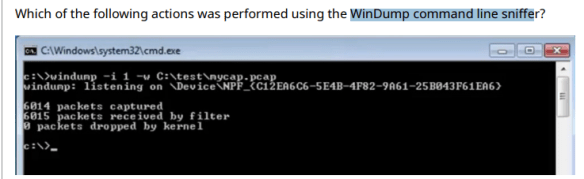
2. WinDump command line sniffer
Requested that hexadecimal strings be included from interface 1 to mycap.pcap.
The command line request is to collect packet capture files from -I (interface) and -w (write) them to the C:testmycap.pcap file.
The read request on interface 1 would be -I 1 -r C:testmycap.pcap.
The hexadecimal string output is the -x option, which is not requested in this capture command.
The asci string output is the -a option, which is not requested in this capture command.
3. using Ettercap in an attempt to spoof DNS
To successfully complete the configuration of your DNS spoofing test, you need to select the ARP poisoning option. ARP requests and replies are sent to victims to poison their ARP cache. Once the cache has been poisoned, the victim sends all packets to the attacker, who modifies them and forwards them to the real destination.
Port stealing is used to sniff a switched environment when ARP poisoning is not effective (for example, where static mapped ARPs are used).
DHCP spoofing pretends to be a DHCP server and tries to force the client to accept the attacker’s reply.
NDP poisoning is only supported if IPv6 support is enabled. ND requests and replies are sent to victims to poison their neighbor cache. Once the cache has been poisoned, the victims send all IPv6 packets to the attacker, who can modify them and forward them to the real destination.
4. MAC Address Poisoning
- Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) poisoning is when an attacker sends fake ARP messages to link their MAC address with the IP address of a legitimate computer or server on the network. Once their MAC address is linked to an authentic IP address, the attacker can receive any messages directed to the legitimate address. As a result, the attacker can intercept, modify, or block communications to the legitimate MAC address
- Port mirroring creates a duplicate of all network traffic on a port and sends it to another device.
- MAC flooding is when an attacker intentionally floods a content addressable memory table with Ethernet frames, each originating from different MAC addresses. Once the table starts to overflow, the switch responds by broadcasting all incoming data to all ports, basically turning itself into a hub instead of a switch.
- MAC spoofing is done to enable bypassing of access control lists on servers or routers by either hiding a computer on a network or by allowing it to impersonate another network device.
5. using tcpdump to capture suspicious traffic detected on port 443 of a server.
- -SX is the command line options for both full packet capture and hexadecimal and ascii output of port 443.
- The tcpdump src port will capture source port traffic on 443 but will not capture the entire packet or output the hexadecimal and ascii codes.
- -SA will capture full packets, but only ascii output is included.
- -SXX performs the same function as -SX and also gives the Ethernet header
6. Wireshark Filtering
- The ne filter stands for not equal. This (ip.src ne 192.168.142.3) command will display all traffic not equal to 192.168.142.3.
- == stands for equal to, && stands for and, and eq is another way to write equal to.
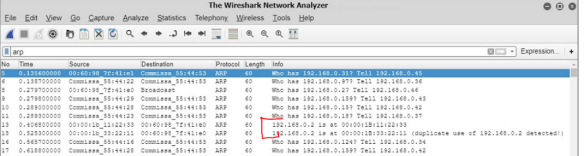
7. Wireshark
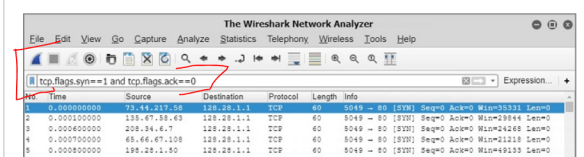
When using Wireshark to detect ARP poisoning, Wireshark displays a duplicate use of IPs detected.
Even without this message, seeing two packets with the same IP address is a good indication that ARP poisoning is taking place on your network
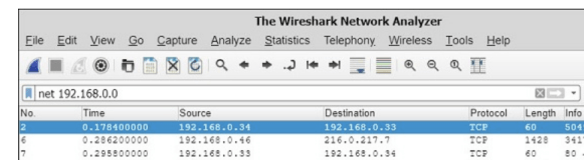
8. Wireshark Filters
The net filter captures traffic to or from a range of IP addresses. Since the network address of 192.168.0.0 was used, only packets with either a source or destination address on the 192.168.0.0 network are displayed.
- image005
- image006
- image007
9. Wireshark Host filter
10. Wireshark Password filter
- image009
- image010
11. Using the tcp contains Invoice filter
12. Company Requestions Payment
13. Best Countermeasure for sniffing
Using encryption methods is the best practice to secure network traffic in this scenario. It becomes one of the last lines of defense. If the encryption method used is strong enough, it will take the attacker too long to decrypt the obtained encrypted traffic to be worth the effort.
An IDS is used to detect intrusion and to alert network administrators of attacks. These systems can search for anomalies in network traffic. They send an alert when an intrusion is detected and are not used as a countermeasure to secure network traffic that has already been obtained by an attacker.
Implementing policies and promoting network security awareness training are good countermeasures, but they will not protect the data that has been obtained by an attacker.
Closing unnecessary ports associated with known attacks and only allowing necessary applications to run lessens the attack arena and are good network attack countermeasures. These countermeasures do not secure network traffic already obtained.
14. Countermeasure against sniffing
- Switched networks provide a natural barrier for an attacker using a sniffer. Be sure to configure settings so the switch shuts down a port when the max number of MAC addresses is reached, so MAC flooding isn’t possible.
- Session hijacking is the process of taking over an established connection between a host and a user.
- DNS spoofing, also known as DNS cache poisoning, targets Active Directory or other DNS-reliant networks.
- Packet filtering firewalls look at a packet’s header information to determine legitimate traffic.